publications
2024
- FFStreams_RAL
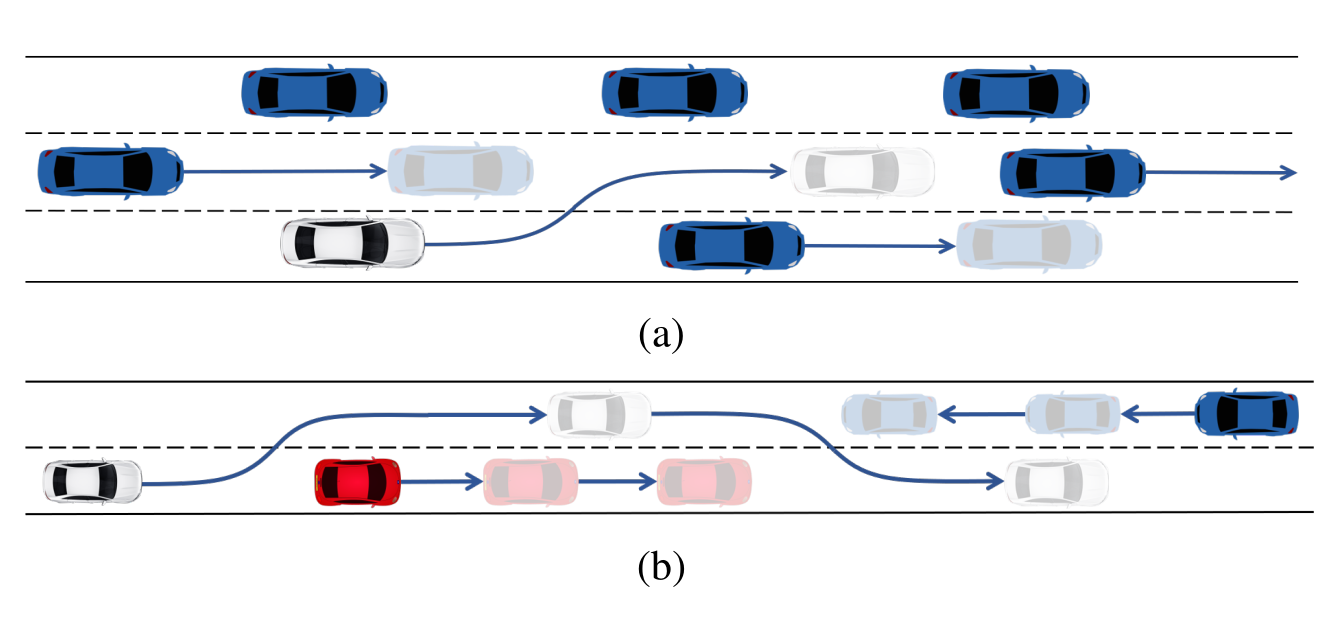 FFStreams: Fast Search with Streams for Autonomous Maneuver PlanningMais Jamal and Aleksandr PanovIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024
FFStreams: Fast Search with Streams for Autonomous Maneuver PlanningMais Jamal and Aleksandr PanovIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024In autonomous driving, maneuver planning is essential for ride safety and comfort, involving both motion planning and decision-making. This paper introduces FFStreams, a novel approach combining high-level decision-making and low-level motion planning to solve maneuver planning problems while considering kinematic constraints. Addressed as an integrated Task and Motion Planning (TAMP) problem in a dynamic environment, the planner utilizes PDDL, incorporates Streams, and employs Fast-Forward heuristic search. Evaluated against baseline methods in challenging overtaking and lane-changing scenarios, FFStreams demonstrates superior performance, highlighting its potential for real-world applications.
@article{Jamal2024, title = {FFStreams: Fast Search with Streams for Autonomous Maneuver Planning}, volume = {9}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10552884}, doi = {10.1109/LRA.2024.3412633}, pages = {6752--6759}, number = {7}, journal = {IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters}, author = {Jamal, Mais and Panov, Aleksandr}, year = {2024}, } - FFStreams++_Predict
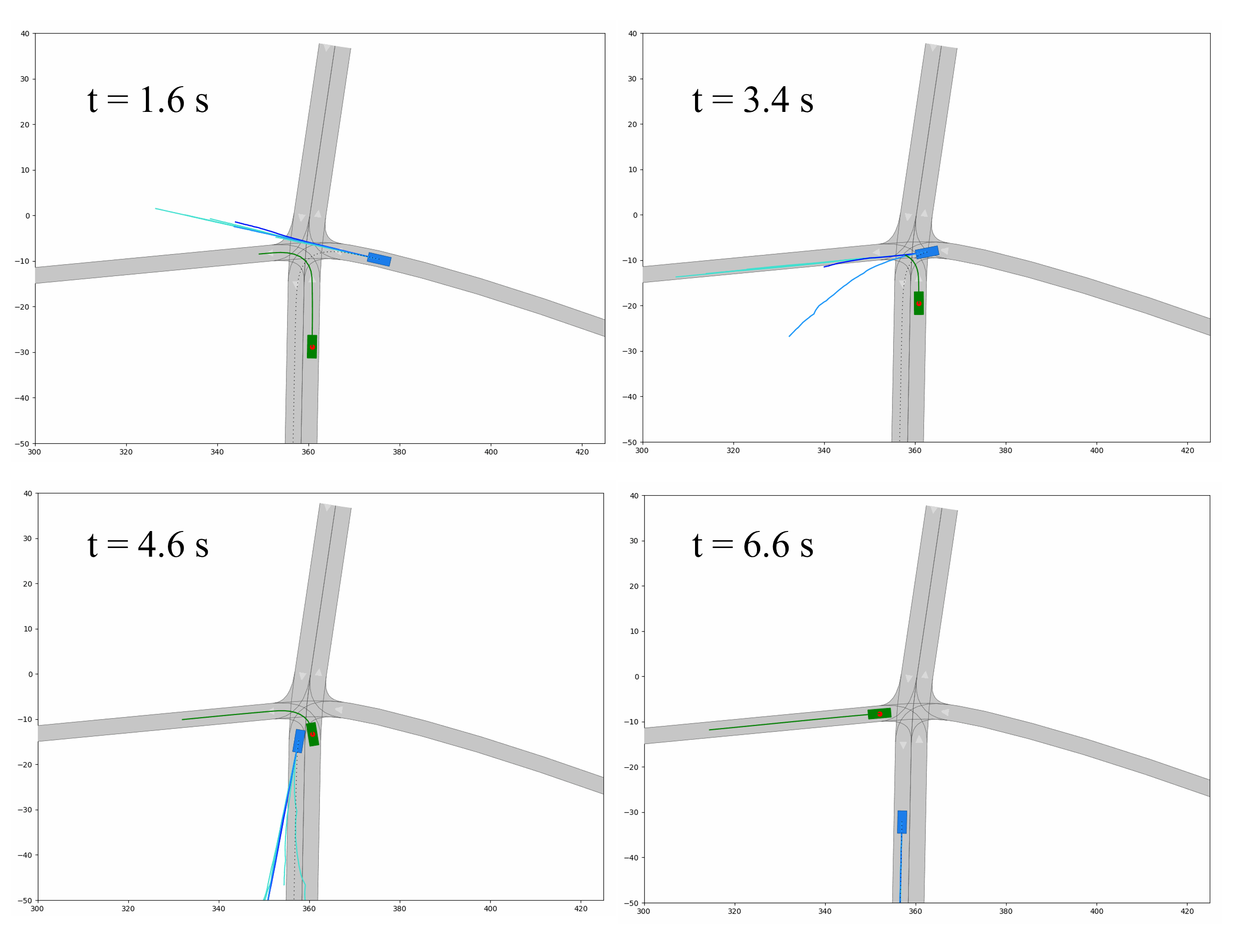 Maneuver Decision-Making with Trajectory Streams Prediction for Autonomous VehiclesMais Jamal and Aleksandr Panov2024
Maneuver Decision-Making with Trajectory Streams Prediction for Autonomous VehiclesMais Jamal and Aleksandr Panov2024Decision-making, motion planning, and trajectory prediction are crucial in autonomous driving systems. By accurately forecasting the movements of other road users, the decision-making capabilities of the autonomous system can be enhanced, making it more effective in responding to dynamic and unpredictable environments and more adaptive to diverse road scenarios. This paper presents the FFStreams++ approach for decision-making and motion planning of different maneuvers, including unprotected left turn, overtaking, and keep-lane. FFStreams++ is a combination of sampling-based and search-based approaches, where iteratively new sampled trajectories for different maneuvers are generated and optimized, and afterward, a heuristic search planner is called, searching for an optimal plan. We model the autonomous diving system in the Planning Domain Definition Language (PDDL) and search for the optimal plan using a heuristic Fast-Forward planner. In this approach, the initial state of the problem is modified iteratively through streams, which will generate maneuver-specific trajectory candidates, increasing the iterating level until an optimal plan is found. FFStreams++ integrates a query-connected network model for predicting possible future trajectories for each surrounding obstacle along with their probabilities. The proposed approach was tested on the CommonRoad simulation framework. We use a collection of randomly generated driving scenarios for overtaking and unprotected left turns at intersections to evaluate the FFStreams++ planner. The test results confirmed that the proposed approach can effectively execute various maneuvers to ensure safety and reduce the risk of collisions with nearby traffic agents.
@article{jamal2024maneuver, title = {Maneuver Decision-Making with Trajectory Streams Prediction for Autonomous Vehicles}, author = {Jamal, Mais and Panov, Aleksandr}, year = {2024}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.RO}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.10165}, }
2023
- RL_Parking
 Learning Adaptive Parking Maneuvers for Self-driving CarsGregory Gorbov, Mais Jamal, and Aleksandr I. PanovIn Proceedings of the Sixth International Scientific Conference “Intelligent Information Technologies for Industry” (IITI’22), 2023
Learning Adaptive Parking Maneuvers for Self-driving CarsGregory Gorbov, Mais Jamal, and Aleksandr I. PanovIn Proceedings of the Sixth International Scientific Conference “Intelligent Information Technologies for Industry” (IITI’22), 2023This paper addresses the autonomous parking for a vehicle in environments with static and dynamic obstacles. Although parking maneuvering has reached the level of fully automated valet parking, there are still many challenges to realize the parking motion planning in the presence of dynamic obstacles. One of the most famous autonomous driving platforms is the Baidu Apollo platform. In the Apollo platform, this problem is solved using the classic method hybrid A*. However, this method has two main downsides. Firstly, it generates in some parking scenarios, trajectories that consist of many partitions with different gear types and sizes. Such trajectories are intractable by a self-driving car when testing the Apollo planner on more realistic data coming from a simulator such as SVL. Secondly, the built-in algorithm does not have the ability to interact with dynamic obstacles, which might lead to a collision in some critical parking scenarios. To overcome these issues, we proposed a method based on reinforcement learning, which uses the RL-policy (from POLAMP) allowing us to take into account the kinematic constraints of the vehicle, static and dynamic obstacles. The proposed method was fully integrated into the Apollo platform with developed Cyber RT nodes, which were used for publishing the parking trajectory from our algorithm to the SVL simulator through a ROS/Cyber bridge. The final model demonstrates transferability to the previously unseen experimental environments and flexibility with respect to built-in hybrid A*.
@inproceedings{10.1007/978-3-031-19620-1_27, author = {Gorbov, Gregory and Jamal, Mais and Panov, Aleksandr I.}, editor = {Kovalev, Sergey and Sukhanov, Andrey and Akperov, Imran and Ozdemir, Sebnem}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-031-19620-1_27}, title = {Learning Adaptive Parking Maneuvers for Self-driving Cars}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the Sixth International Scientific Conference ``Intelligent Information Technologies for Industry'' (IITI'22)}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, address = {Cham}, pages = {283--292}, isbn = {978-3-031-19620-1}, url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-19620-1_27}, }
2021
- AdaptBehaviorTree
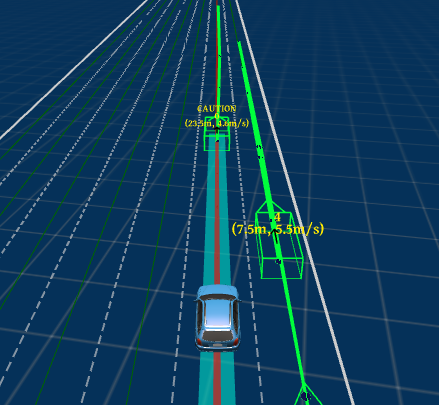 Adaptive maneuver planning for autonomous vehicles using behavior tree on apollo platformMais Jamal and Aleksandr PanovIn Artificial Intelligence XXXVIII, 2021
Adaptive maneuver planning for autonomous vehicles using behavior tree on apollo platformMais Jamal and Aleksandr PanovIn Artificial Intelligence XXXVIII, 2021In safety-critical systems such as autonomous driving systems, behavior planning is a significant challenge. The presence of numerous dynamic obstacles makes the driving environment unpredictable. The planning algorithm should be safe, reactive, and adaptable to environmental changes. The paper presents an adaptive maneuver planning algorithm based on an evolving behavior tree created with genetic programming. In addition, we make a technical contribution to the Baidu Apollo autonomous driving platform, allowing the platform to test and develop overtaking maneuver planning algorithms.
@inproceedings{jamal2021adaptive, title = {Adaptive maneuver planning for autonomous vehicles using behavior tree on apollo platform}, author = {Jamal, Mais and Panov, Aleksandr}, booktitle = {Artificial Intelligence XXXVIII}, publisher = {Springer, Cham}, address = {Cham}, volume = {13101}, pages = {327--340}, year = {2021}, isbn = {978-3-030-91100-3}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-030-91100-3_26}, url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-91100-3_26}, }
2019
- Quadcopter
 Low-Cost Quadcopter Indoor Positioning System Based on Image Processing and Neural NetworksI. Hatem, M. Jamal, Y. Murhij, and 1 more authorIn Mechanism, Machine, Robotics and Mechatronics Sciences, 2019
Low-Cost Quadcopter Indoor Positioning System Based on Image Processing and Neural NetworksI. Hatem, M. Jamal, Y. Murhij, and 1 more authorIn Mechanism, Machine, Robotics and Mechatronics Sciences, 2019Quadcopter positioning in indoor environments is considered a major problem because of the difficulty of estimating a reliable position. Moreover, the positioning system is expected to work in real-time and to be accurate and cost-effective. In this paper, a combination of image processing techniques and neural networks is proposed to obtain the quadcopter position along the X, Y and Z coordinates. Three neural networks were used, one for each dimension. The proposed neural network based technique estimates the quadcopter target position along X, Y, and Z from two image points extracted from images captured by two low-cost IP cameras. The offered positioning system has been implemented on a locally designed and assembled quadcopter. Hovering experiments on the quadcopter have been performed in an indoor lab based environment. The results show that combining image processing techniques with neural network-based method achieves a low-cost accurate positioning system within a precision of a few centimeters with a frequency of 16 Hz.
@inproceedings{10.1007/978-3-319-89911-4_18, author = {Hatem, I. and Jamal, M. and Murhij, Y. and Ali, Z.}, editor = {Rizk, Rany and Awad, Mariette}, title = {Low-Cost Quadcopter Indoor Positioning System Based on Image Processing and Neural Networks}, booktitle = {Mechanism, Machine, Robotics and Mechatronics Sciences}, year = {2019}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, address = {Cham}, pages = {243--257}, isbn = {978-3-319-89911-4}, url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-89911-4_18}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-319-89911-4_18}, }




